头文件
#ifndef PETERSON_ALGO_H
#define PETERSON_ALGO_H
#include <atomic>
class PetersonMutex {
public:
PetersonMutex();
void lock(int threadId);
void unlock(int threadId);
private:
std::atomic<bool> flag[2]{};
std::atomic<int> turn{};
};
#endif //PETERSON_ALGO_H
函数实现
#include "peterson_algo.h"
PetersonMutex::PetersonMutex() {
flag[0].store(false);
flag[1].store(false);
turn.store(0);
}
void PetersonMutex::lock(int threadId) {
int otherThreadId = 1 - threadId;
flag[threadId].store(true);
turn.store(otherThreadId, std::memory_order_relaxed); //指定了内存顺序为`std::memory_order_relaxed`,这表示不需要特定的内存顺序,仅确保写操作是原子的
while (flag[otherThreadId].load() && turn.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) == otherThreadId) {
// busy waiting
}
}
void PetersonMutex::unlock(int threadId) {
flag[threadId].store(false, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
调用测试
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include "peterson_algo.h"
PetersonMutex mutex;
const int NUM_ITERATIONS = 5;
void P0() {
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_ITERATIONS; ++i) {
mutex.lock(0);
std::cout << "Thread P0 entered critical section." << std::endl;
// Simulating some work inside critical section
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(500));
std::cout << "Thread P0 exited critical section." << std::endl;
mutex.unlock(0);
// Rest of the code
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(300));
}
}
void P1() {
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_ITERATIONS; ++i) {
mutex.lock(1);
std::cout << "Thread P1 entered critical section." << std::endl;
// Simulating some work inside critical section
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(300));
std::cout << "Thread P1 exited critical section." << std::endl;
mutex.unlock(1);
// Rest of the code
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(500));
}
}
int main() {
std::thread threadP0(P0);
std::thread threadP1(P1);
threadP0.join();
threadP1.join();
return 0;
}
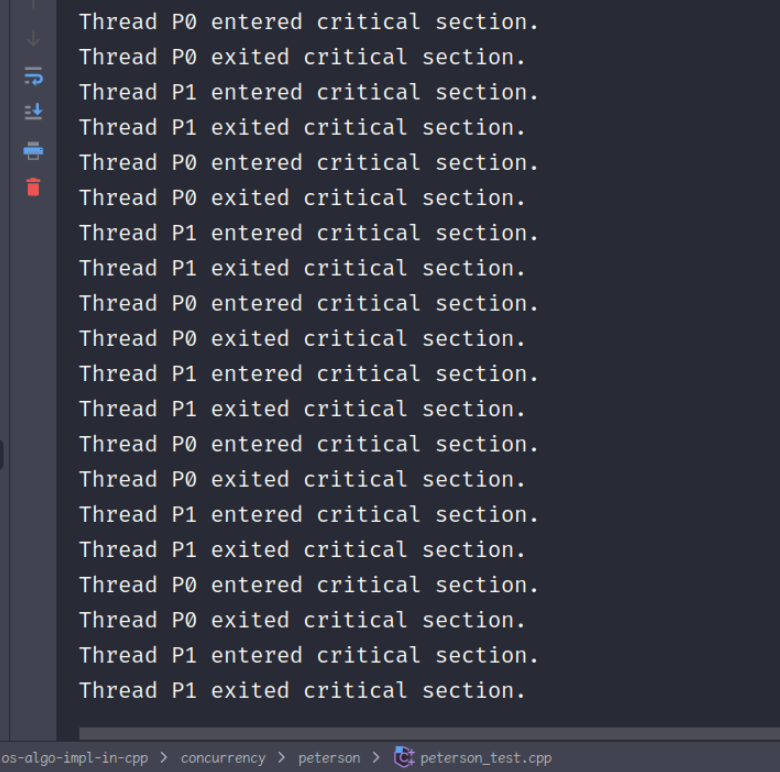
输出结果