Introduction
ECMP/WCMP 是大规模 IP 网络(Datacenter or WAN)中事实上的流量负载均衡标准。
Traffic/Forwarding Polarization: different switches repeatedly use the same hashing algorithm, resulting in a switch selecting a small portion of links for all traffic destined for one prefix, while other links were underutilized.
hash correlation: describe the association between hash functions in different switches that leads to traffic polarization.
已有一些方案用户缓解散列相关性:
- 一类方案是使用 hash 函数的变体,例如使用不同的 seeds ,但后文可以论证这个方案并不有效。
- 使用包头部的 TTL 字段进行 hash 。
Background and Motivation
The implications of bad hashing are twofold.
- First, bad hashing leads to traffic polarization that endangers reliability (due to reduced path diversity), wastes network bandwidth, cancels efficiency gains of traffic engineering, and inevitably increases network cost.
- Second, bad hashing causes inherent traffic load imbalance and leads to network congestion that affects application performance.
Hashing is a Practical Challenge in Network Designs
现代网络中 hash 已经是一个日益重要的问题:
- 规模庞大:both datacenter and WANs are getting bigger with more switches and stages;
- 路径密集:modern networks are very dense and have a large number of paths between any two nodes
- topology and routing become more agile and flexible in order to improve network efficiency and availability, e.g., the move from spinefull DCN to reconfigurable spineless [13, 32] and the use of non-shortest path routing to improve availability and performance [15];
- emerging applications (such as distributed machine learning) are becoming more throughput hungry while demanding stricter network SLA guarantees.
Multi-stage Clos DCN
现代 DCN 连接着大量计算/存储节点,运行着关键服务,如搜索、视频、地理与地图、云和游戏等,并且具有非常大的路径多样性(path diversity);因此,散列和流量负载平衡至关重要。
在此处使用 Jupiter 拓扑作为多阶段 Clos DCN 的样例,如下图 Fig 1 。
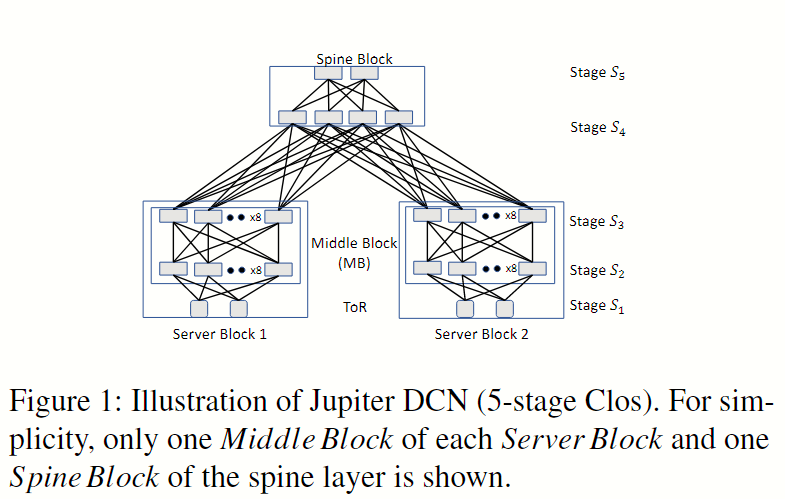
Jupiter 中有 Server Block(后文记作 SB)、5 个交换机阶段(分别记作 ),因此当一个包从 中的 ToR 路由到 中的另一个 ToR 时,最长的转发路径及其跳序列是 。为了实现最佳的负载均衡,hash 需要满足这样的属性:相同转发路径上不应有相关的 hash 函数。直觉上,我们需要 (准确说是 最大跳数-1)个独立 hash 函数,这里 指的是框架的层数或阶段数。
在 Jupiter 中需要 8 种 hash 函数,但不幸的是其交换机只有 6 种不相关 hash 函数,因此我们需要减少多阶段 Clos DCN 对 hash 函数数量的需求。
Spineless DCN
在数据中心网络(Datacenter Network, DCN)中,spineless 通常描述一种特定的网络架构或网络拓扑的特性,指的是网络中的交换结构没有一个中心的核心或骨干(spine)。它与传统的 spine-leaf 架构相对。
传统的 Spine-Leaf 架构
Spine-leaf 是数据中心常见的一种网络拓扑结构,由两个层次的交换机组成:
- Spine 层:核心层交换机,负责高性能的数据转发。所有叶交换机(Leaf)通过 Spine 交换机互联,保证网络冗余性和高可用性。
- Leaf 层:接入层交换机,连接服务器等设备,通常每个 Leaf 都与每个 Spine 交换机相连,形成一个全互连的网络。
在这种架构中,Spine 层充当了整个网络的骨干和核心,所以有时称为“有脊”(spine)的网络。
Spineless 网络
相对的,spineless 数据中心网络没有 Spine 层,这意味着网络不依赖一个核心层或骨干结构。它通常基于扁平化、去中心化的网络设计,多个交换机相互对等连接,没有明显的层次划分。这种架构的几个特点包括:
- 扁平化架构:整个网络层次减少,降低了延迟,因为不再需要经过核心交换机层。
- 去中心化:没有单一的核心交换机作为流量的汇聚点,每个交换机承担的角色相对均衡。
- 高扩展性:通过添加更多对等交换机的方式扩展网络,而不会形成性能瓶颈。
- 网络弹性:由于去除了中心节点,减少了单点故障,网络的容错性和稳定性可能更高。
Spineless 网络有时也与软件定义网络(SDN)结合使用,使得网络中的交换机动态调整和分配资源,进一步提升网络性能。

Spineless DCN 是新兴的拓扑,能够减少开销并支持更快的技术更新,但是需要 hash 函数也更多。在 spineless DCN 中,server block 通过 mesh 结构直接连接,spine block 被完全移除以降低网络成本。同时采用非最短路径路由以增强了路由差异性,从而实现高可用性,并使得流量工程能够优化网络链路的利用率。
尽管 spineless DCN 成本低、效率高,但 hash 设计却更具挑战,因为所需 hash 函数的数量取决于 server block 的数量,而不是多级 DCN 的层数。以 Gemini[^1] 为例,假设我们在路由中最多只允许一个中转 server block,那么数据包的最长转发路径是:,这里 是随机选择的三个服务器区块的索引。此时关键挑战就是确保任意 的 server block 组合中没有相关联的 hash 函数,因此 spineless DCN 需要 量级的 hash 函数,此处 是 server block 的数量。在经典结构中, 的范围在 10 到 100 之间,因此使用当前一代交换机提供的有限 hash 函数来设计 hash 非常具有挑战性。
WAN
流量工程和负载均衡对于提高 WAN 性能和降低运营成本至关重要。网状连接(mesh)的 WAN 在 hashing 设计方面也面临同样的挑战,即所需的不相关 hash 函数的数量取决于网络的规模。
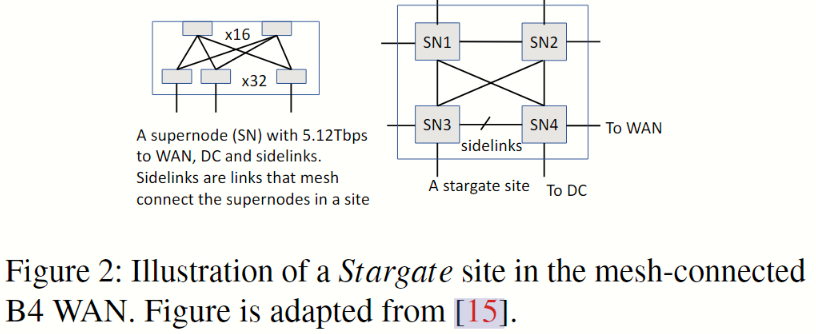
Fig 2 显示了 B4 WAN Stargate 站点的拓扑结构。每个站点最多由 4 个超级节点组成,其中每个超级节点是一个两级 Clos 网络,与广域网、数据中心和同一站点的其他超级节点连接。B4 站点级拓扑结构是一个部分连接的网状结构,采用非最短路径路由。
与 spineless DCN 类似,WAN 中也需要 量级的 hash 函数, 是 WAN 中站点的数量。需要注意的是,2012 2017 年间 B4 WAN 的规模增加了 7 倍,因此 hashing 问题颇具挑战。
ECMP/WCMP Traffic Load Balance
ECMP 策略的简介
Equal-Cost Multiple-Path (ECMP) – a routing and traffic load balancing strategy that allows traffic between a source and destination node to be transmitted across multiple paths – identifies a set of routes, each of which is equal-cost towards the destination. The routes identified are referred to as anECMP group. An ECMP group is defined at flow-level. When forwarding a packet, the routing strategy decides which nexthop path to use based on a hashing algorithm. That is, the route of a packet is determined by the mapping from the hash value to an egress port, i.e., h % n, where h is the hash value, and n is the number of output ports in the ECMP group.
常见的用于 hash 输入的 IP 包头字段有:source IP、destination IP、transport protocol、TCP/UDP ports、IPv6 flow label。
Hash Correlation Causes Traffic Polarization and Load Imbalance
Limited Number of Hash Functions Leads to Hash Correlation.
Random Seeds Are Not Effective.
Applying a random seed is a linear operation and it can not decorrelate a hash function’s output effectively.
Hashing Design in Multi-stage Networks
Strawman solution: per-stage hashing
Per-port hashing
Color recombining
Hashing design for multi-stage Clos does not work in spineless DCNs and WANs
Mitigating Correlation for Mesh Networks
The Coprime Theorem
互素理论的关键思想是,互素数进行模运算会使哈希函数的输出不相关。
考虑到一个哈希函数 散列结果的值域为 ,我们应用两个互素数的模运算,从 得出两个独立的哈希函数 和 ,其中 为最大的散列值。
在交换机中,我们使用哈希函数通过执行模运算来选择下一跳,即 ,其中 是数据包 的哈希值, 是 ECMP 或 WCMP 组中下一跳的数量。考虑这样的场景:在一条转发路径上有两个交换机,它们都选择哈希函数 选取下一跳,这样就像 Fig 4b 中提到的那样发生散列相关和流量极化现象。如公式 1 所示,在这两个开关中使用的是相同的哈希函数 ,我们可以在第一个交换机上使用导出的 ()从 个下一跳中选择一个作为下一跳,而在第二个交换机上使用 ()从 个下一跳中选择一个作为下一跳。
定理 2 表明这两个哈希函数没有相关性:
&\textbf{Theorem 2} \text{}\\ & \forall i,j, \text{Prob}(H_{2}(x)\%m_{2}=j|H_{1}(x)\%m_{1}=i) \simeq \text{Prob}(H_{2}(x)\%m_{2}=j)\\ & \text{if the following two conditions are satisfied:}\\ &\textit{Condition 1: } q_{1}\gg m_{1} \text{ or } q_{1}\%m_{1}=0,\text{ and }q_{2}\gg m_{2} \text{ or } q_{2}\%m_{2}=0; \\ &\textit{Condition 2: } \hat{H}\gg q_{1}q_{2} \text{}\\ & \text{where }q_{1}\text{ and }q_{2}\text{ are two coprime values, }\\ &m_{1}\text{ and }m_{2}\text{ are the number of next hops, and }x\text{ is a packet.}\\ &\textbf{用简要的中文描述:}\text{}\\ \end{align*}$$ 该定理表明,对于输入 $x$,当选择适当的共素数 $q_1$ 和 $q_2$ 时($q_1$ 和 $q_2$ 的选择应满足定理 2 的条件 1 和 2),$H_2\%m_2$ 的哈希值与 $H_1\%m_1$ 的哈希值是独立的。定理 2 的证明见附录。 ### Coprime for ECMP 当两个哈希函数相关时,我们只需选择两个共素数,然后应用额外的模运算,就能得到两个独立的哈希函数,如公式 1 所示。 在交换机中为散列值添加额外的调制运算似乎既直观又简单,但这需要对交换机硬件进行修改,而我们使用的交换机芯片并不提供这种功能。即使交换机供应商在其下一代芯片中提供这种功能,我们也必须更换所有现有的交换机,这将是一项艰巨而昂贵的任务。 相反,我们提出:复制 ECMP 组条目,以匹配 SDN 控制器中的互素值,并通过现有的 OpenFlow 接口与交换机流量表和组表进行交互。图 11 显示了该方法的流程。 ![[Hashing Design in Modern Networksnotes-fig11-apply-coprime.png]] 我们用一个例子来解释。假设 IP 前缀 `10.1.2.0/24` 的 ECMP 组中有两个出口端口。 假设发生一次哈希相关,我们选择 5 的共素值来减轻哈希相关性。我们不需要修改交换机硬件来实现两次模运算 $h\%5\%2$(h 是散列函数返回的散列值)以选择出口端口,而是在 ECMP 组中将 2 个物理端口复制为 5 个逻辑端口。这样,我们只需进行一次模操作(即 $h\%5$)即可确定逻辑端口,并最终确定物理出口。目前的商品交换机都支持复制 ECMP 组条目以匹配互素值,我们只需在 SDN 控制器中添加少量逻辑即可。请注意,图 11 显示,一个流量表包含许多 IP 前缀/流量,它们共享交换机中的同一个组(多路径)表,因此我们需要在 $\text{hash value \% group size}$ 上添加一个偏移量,以索引每个 IP 前缀/流量。 上述互素 ECMP 分组大小方法有两个技术难题: 1) 交换机内存使用量增加,特别是在共素值较大的情况下。 内存使用量增加了 $\mathcal{O} (\frac{q}{m})$ 倍,其中 $q$ 和 $m$ 分别是互素数和原始 ECMP 组大小; 2) ECMP 精度损失,即 ECMP 组中不同出口端口的预期权重和实际权重之间的差异。 为了节省交换机内存,我们可能希望选择较小的共素值。 但是,小的共素值与定理 2 中的条件 1 相矛盾;此外,我们还需要容忍小的共素值带来的 ECMP 精度损失。 在计算 ECMP 分组大小时,有些端口会重复 $⌊q/m⌋$ 次,有些端口会重复 $⌊q/m⌋ + 1$ 次。 因此,当 $q/m$ 较小时,会带来 ECMP 精度损失。 我们使用变异系数 (CV,coefficient of variation) 来衡量互素值的有效性。假设我们有 $m$ 个链路,每个链路的预期流量为 $p_{i} = \frac{1}{m}$ 。使用互素值 $q$ 后,实际流量分布为 $\hat{pi} = (⌊q/m⌋ + I (i ≤q\%m))/q$ ,其中 $I (.)$ 为指示函数,$i∈\{0, m - 1\}$ 为端口 id,当 $i≤q\%m$ 时,$I (. ) = 1$。 CV 是针对 $\hat{pi}$ 计算的。 在我们的共素法实现过程中,我们在遵守交换芯片提供的 ECMP 表大小限制的同时,最大限度地降低了 CV。 ### Coprime for WCMP 正如文献[37]所述,链路或交换机故障导致的拓扑不对称要求加权成本多路径(WCMP)根据下游跳数的能力按比例分配流量。 在本节中,我们将把基于互素的方法从 ECMP 扩展到 WCMP。 一种简单直接的方法是将 WCMP 组视为由 W 个 ECMP 端口组成的 ECMP 组,其中 W 是权重之和,即 $W = ∑_i w_i$,$w_i$ 是端口 $i$ 的权重,我们将 W 个 ECMP 端口复制为 q 个逻辑端口,就像 ECMP 组一样,其中 q 是一个共素值。但是,复制后的权重可能与预期的 WCMP 权重有很大偏差。 一个例子如图 12 a 所示: ![[Hashing Design in Modern Networksnotes-fig12-coprime-for-wcmp.png]] WCMP 组中有两个端口,它们的权重分别为 3 和 1,即 $w_1 = 3$ 和 $w_2 = 1$ 。这个 WCMP 组可视为一个 ECMP 组,其中 W = 4 个 ECMP 端口。 假设我们选择一个互素值 7,复制后的实际权重为 $\hat{w_1} = 6$ 和 $\hat{w_2} = 1$,这与预期的 WCMP 权重相差很大。 我们使用 $\{\hat{w_{i}}/w_{i}\}$ 的 CV 值来量化差异。 如图 12 a 所示,CV 为 0.33。 为了减小 WCMP 组大小互素处理后的实际权重与预期 WCMP 权重之间的差异,我们提出了一种改进算法来重复 WCMP 组中的条目,记作 *split coprime* 。假设 WCMP 组有 m 个端口,端口 $i$ 的权重为 $w_i$,$W = ∑_i w_i$,选择的互素值为 q。我们将互素值拆分为两部分:$ˆq = a ∗ W$ 和 $r = q\%W$ ,其中 $a = ⌊q/W ⌋$。 直观的做法是将端口复制到 $ˆq$ 逻辑端口,也就是说,每个 WCMP 端口都被复制了 $w_i ∗ a$ 次。 我们按以下方式将 m 个端口复制到左侧 $r$ 个条目:每个端口 $i$ 复制 $⌊r/m⌋+I (i < r\%m)$ 次,其中 $I (.)$ 是一个指示函数,当 $i < r\%m$ 时,$i∈ \{0, 1, ..., m - 1\}$,$I (.) = 1$ 。 图 12 展示了一个 WCMP 分组的互素化过程:对于 ˆq,两个 WCMP 端口复制 $w_i$ 次,$w_1 = 3$,$w_2 = 1$;对于 r,端口 1 复制 2 次,端口 1 复制 1 次。 采用这种改进算法后,CV 值比简单地将 WCMP 组视为 ECMP 组的方法要小得多。 对于 WCMP,互素化的内存成本可以忽略不计,因为即使没有互素化,我们也需要进行 WCMP 量化(即通过复制 ECMP 表项来近似小数权重)[37],以确保组中的 WCMP 项数不超过预定义的限制。 ## Evaluation ### Experiment Setup **流量跟踪**。 **网络拓扑**。 **哈希函数**。 **度量参数**。 ### Color Recombining for Multi-stage DCN 我们首先研究了针对多级 DCN 提出的**带有颜色重组的逐端口散列**(以下简称为颜色重组)方案的流量负载平衡性能,并与**带有随机种子的逐阶段散列**(以下简称为每级散列)进行了比较。对于每阶段散列,我们为每个阶段分配一个独立的散列函数,并用随机种子初始化每个散列函数。 ![[Hashing Design in Modern Networksnotes-fig13-link-utilization.png]] 图 13 显示了一个 ECMP 组中八个链路的归一化链路利用率。 从图中可以看出,在颜色重组中,所有 8 个链路的链路利用率都差不多,都在 0.67 左右,但每阶段散列方法却显示出严重的不均匀性。 在颜色重组中,我们只在颜色重组发生时重复使用哈希函数,这就消除了哈希相关性;但在每阶段散列中,某些哈希函数在不考虑相关性的情况下被重复使用,而且随机种子是线性运算,无法对重复使用的哈希函数进行装饰。 我们还计算了每个 ECMP 组的 CV,并在图 14 中绘制了 CV 的 CDF。 ![[Hashing Design in Modern Networksnotes-fig14-CV-CDF.png]] 所有颜色重组的 CV 值都低于 0.05,但每阶段散列的 CV 值可能高于 0.6(注意,CV 值为 1 意味着标准偏差等于平均值)。 换句话说,与使用随机种子的每级散列相比,使用颜色重组方法的每端口散列可将 CV 值降低约一个数量级。较大的 CV 值意味着同一 ECMP 组中的链路没有得到合理利用,导致网络容量浪费和不必要的热链路,从而在大流量负载下造成网络拥塞。 ### Coprime for Spineless DCN 在 spineless DCN 中,所有八个服务器区块都以 DRing 拓扑连接[13]。 我们为每对服务器块选择两个共素值,以减轻它们之间的哈希相关性。 我们将互素方案与每级散列进行了比较,在每级散列中,每个服务器块使用 3 个从 RTAG 7 散列系列中随机选择的散列函数,每个函数都有一个随机种子。 我们进行了实验,以评估基于互素的 ECMP 和 WCMP 方法。 **Coprime for ECMP**. 图 20 显示了连接两个服务器区块的 16 条链路的归一化链路利用率。 ![[Hashing Design in Modern Networksnotes-fig20-coprime-link-utilization.png]] 所有链接的利用率都在 0.75 左右,其中,两个服务器区块的互素值分别为 8(注意每个 ECMP 组有 8 个端口,因为服务器区块的每个 $S_3$ 芯片有 8 个向上的端口)和 57。 然而,使用每级哈希算法,最大/最小链路利用率的比值都高于 2。 由于缺少独立的散列函数,每级散列不得不重复使用某些相同的散列函数(即使这些散列函数带有随机种子),这就导致了流量极化,如图 20 所示。 在量化方面,基于互素的方法优于每级散列,其 CV 值降低了约 80%。 ![[Hashing Design in Modern Networksnotes-fig14~19-eval.png]] 如图 15 所示,对于基于互素的方法,所有 CV 值都低于 0.1,但对于每级散列,CV 值可能高达 0.5。 在减轻散列相关性时,共素值很重要:**大的共素值比小的更有效**。 我们评估了从 9 到 73 的五个不同的共素值,并在图 16 中显示了 CV。 从图中可以看出,当共素值为 9 时,CV 值接近 0.4。 当共素值增加到 73 时,与 57 相比,改进并不明显。 这一结果与我们在第 4.2 节末尾的分析一致,该分析描述了内存使用和 ECMP 精度之间的权衡。 如何选择 coprime 值取决于交换机的内存和可容忍的不平衡程度。 ### Coprime for WAN ### Hardware Testbed Evaluation and Production Fabric Deployment ## Related Work [^1]: MingyangZhang, et al. Gemini: Practical Reconfigurable Datacenter Networks with Topology and Traffic Engineering.