脱机技术
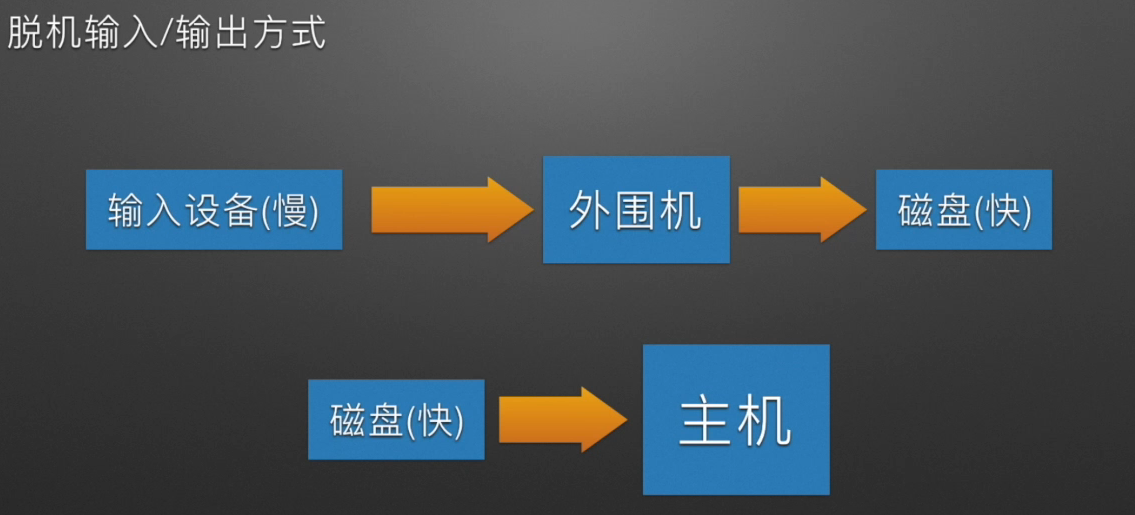
输入设备输入数据的速度远慢于 CPU 处理的速度,这就使得 CPU 资源被浪费。于是使用“中介”来处理 CPU 和 I/O 设备之间速度不匹配的矛盾——把输入输出的工作交给外围机来直接管理,外围机接收到数据后再存放到高速磁盘/磁带中,CPU 从磁盘磁带中读取数据,这使得 CPU 效率明显提升。
因为这个输入和输出的过程是由外围机直接负责的,而不是主机。所以该输入/输出方式脱离了主机,就叫做脱机技术。
假脱机技术
假脱机技术就是通过软件来模拟脱机输入和脱机输出的技术。
在使用脱机技术的时候,用外围机直接接收用户输入的数据。既然它是实体的机器,那么它必然要受到使用环境、自身重量、数量和体积的限制。假如有很多很多输入设备,那么对应的就要有很多很多外围机,这显然是不合理的。
若将实体机器虚拟化,就能摆脱上述问题的限制,将 IO 效率提升一个大台阶,所以假脱机技术应运而生。
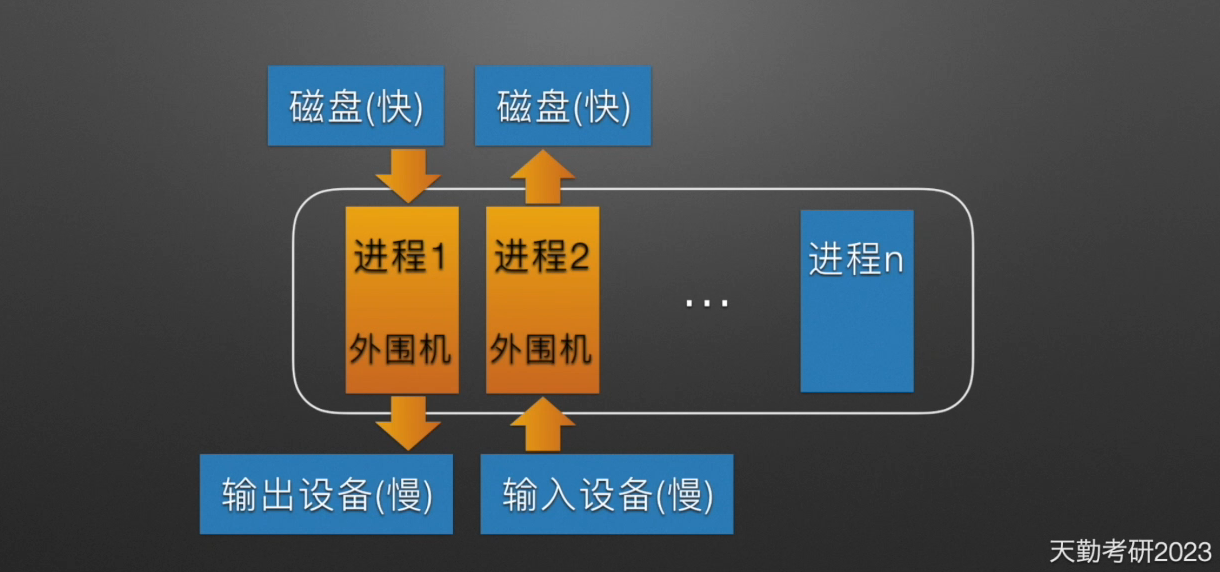
SPOOLing 的意思是同时外设联机操作(Simultaneous Peripheral Operation On-Line),又称为假脱机输入/输出操作。
SPOOLing 是操作系统中采用的一种将独占设备改造为共享设备的技术,所以 SPOOLing 系统必须使用独占设备。 它有效减少了进程等待读入/读出信息的时间,加快了作业执行的速度。
SPOOLing 技术是用软件的方式实现了数据的预输入和缓输出。
SPOOLing 系统的组成
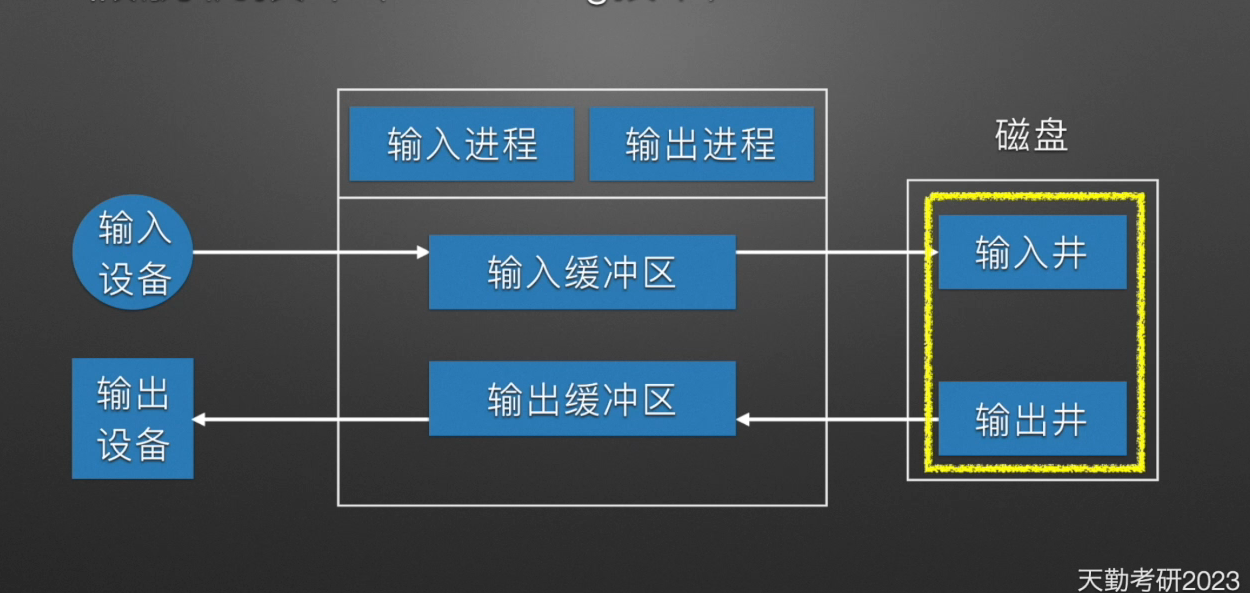 SPOOLing 系统由预输入程序、井管理程序、缓输出程序组成。
SPOOLing 系统由预输入程序、井管理程序、缓输出程序组成。
-
系统在磁盘开辟两个空间,一个输入井,一个输出井。
- 输入井是模拟脱机输入时的磁盘,收容从输入设备输入的这些 IO 数据
- 输出井是模拟脱机输出时的磁盘,收容用户进程输出的数据
-
系统在内存中开辟了两个缓冲区,一个输入缓冲区、一个输出缓冲区。
- 输入缓冲区用于暂存由输入设备传递过来的数据,然后再传到输入井。
- 输出缓冲区用于暂存由输出设备传递过来的数据,然后再传到输出井。
-
输入进程和输出进程
- 输入进程模拟脱机输入时的外围控制机。
- 输出进程模拟脱机输出时的外围控制机。
SPOOLing 系统的输入输出过程
SPOOLing 系统在输入和输出之间增加了“输入井”和“输出井”的排队转储环节,以消除用户的“联机”等待时间。在系统收到作业输入请求信号后,输入进程负责将信息从输入设备中读入输入缓冲区。当缓冲区满时,将信息从缓冲区写到磁盘的输入井中,反复循环,直到一个作业输入完毕。当输入进程读到一个硬件结束标志之后,系统把最后一批信息写入磁盘输入井并调用中断处理程序结束该次输入。然后系统为该作业建立作业控制块,从而使输入井中的作业进入作业等待队列,等待作业调度程序选中后进入内存运行。系统在管理输 入井过程中可以“不断”读进输入的作业,直到输入结束或输入井满而暂停。输出过程与此类似。
SPOOLing 应用举例:共享打印机
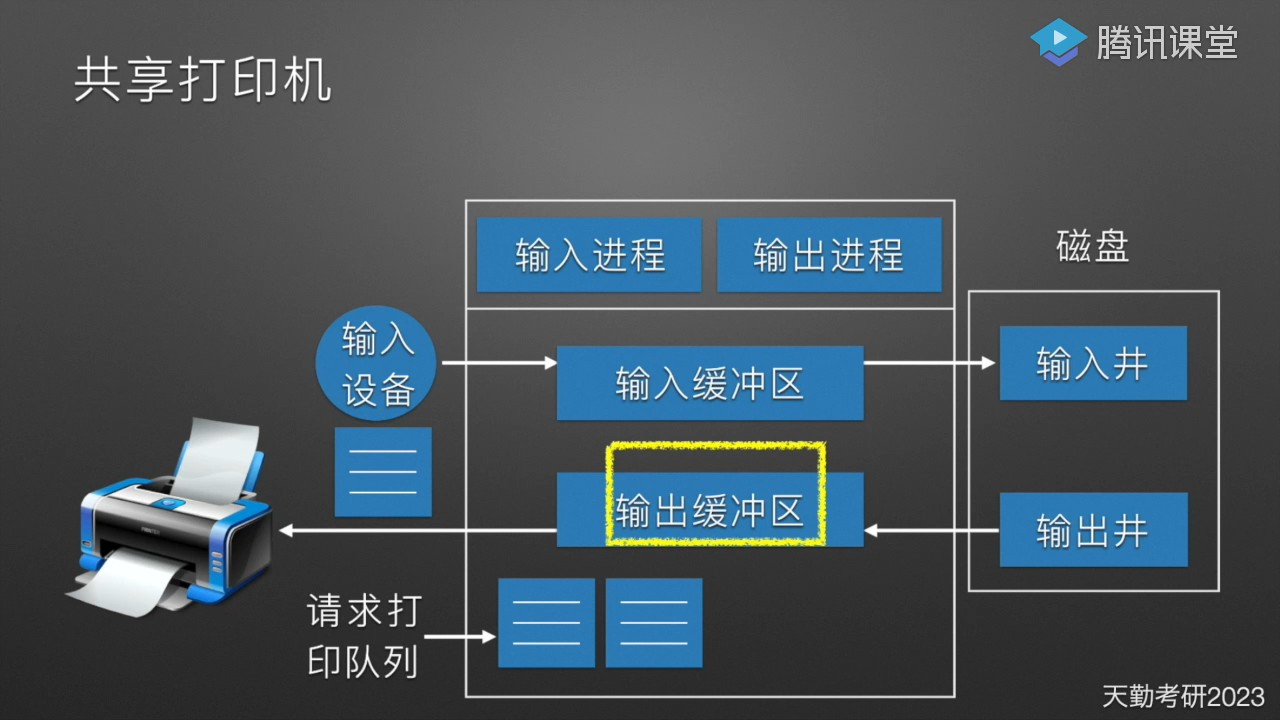 将一台独享打印机改造为可供多个用户共享的打印机,是应用 SPOOLing 技术的典型实例。具体做法是:系统对于用户的打印输出,并不真正把打印机分配给该用户进程,而是先在输出井中申请一个空闲盘块区,并将要打印的数据送入其中:然后为用户申请并填写请求打印表,将该表挂到请求打印队列上。若打印机空闲,输出程序从请求打印队首取表,将要打印的数据从输出井传送到内存缓冲区,再进行打印,直到打印队列为空。
将一台独享打印机改造为可供多个用户共享的打印机,是应用 SPOOLing 技术的典型实例。具体做法是:系统对于用户的打印输出,并不真正把打印机分配给该用户进程,而是先在输出井中申请一个空闲盘块区,并将要打印的数据送入其中:然后为用户申请并填写请求打印表,将该表挂到请求打印队列上。若打印机空闲,输出程序从请求打印队首取表,将要打印的数据从输出井传送到内存缓冲区,再进行打印,直到打印队列为空。
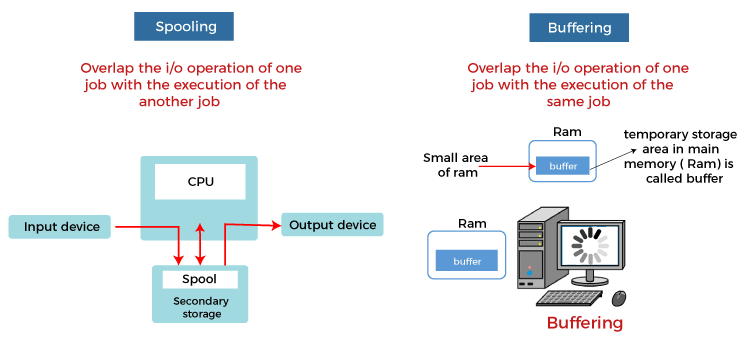
SPOOLing vs. Buffering
| Features | Spooling | Buffering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A spooling is a type of buffer that holds the jobs for a system until the system is ready to accept the jobs. | Buffering is the act of temporarily storing data in a buffer. The buffer is a part of the main memory used to temporarily store or hold data sent between two devices. |
| Resources Requirement | Spooling needs less resource management than buffering because various resources control the process for different jobs. | It needs greater resource management because the same resource handles the process of the same divided job. |
| Efficiency | More efficient | Less efficient |
| Internal Implementation | It overlaps the I/O of one task with the computation of another job. | It overlaps the I/O of one task with the computation of the same task. |
| Remote Processing | It could also process data at remote places. The spooler only needs to be notified when a process is done at the remote site to spool the next process to the remote side device. | It doesn’t support remote processing. |
| Size | It considers the disk as a large spool or buffer. | Buffer is a limited area in the main memory. |
| Usage | It helps in the exchange of data between devices with various data access rates. | It helps in adapting to speed differences between producers and consumers of data streams. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Spooling
Various advantages and disadvantages of spooling are as follows:
-
Advantages
- Idle CPUs are not considered to be very efficient. Most protocols are created to make the best use of the CPU in the shortest period of time. Spooling is similar a process. During spooling, the CPU is kept busy for most of the season, and it only becomes idle when the queue is exhausted. As a result, any tasks that need to be completed can be put in the queue, and the CPU will complete all of them before entering the idle state.
- It makes no difference how many I/O devices or actions there are. Many I/O devices can operate concurrently without interfering with or disrupting one another.
- It enables applications to function at the CPU’s speed while I/O devices operate at their maximum speed.
- During spooling, there is no connection between the input/output devices and the CPU. It means the CPU won’t have to wait for I/O tasks to finish.
- Multiple I/O devices can work simultaneously.
-
Disadvantages
- It’s a technique for copying and running data from a slower to a faster device. The slower device makes a SPOOL to hold the data in a queue processed by the CPU. The technique alone makes Spooling useless in real-time environments where we require real-time results from the CPU. It’s due to the slower input device, which provides data at a slower rate, whereas the CPU can function quicker, allowing it to move on to the next process in the queue. As a result, the final result or output is created later rather than in real-time.
- It requires a huge quantity of storage, which is determined by the number of input requests and the input devices connected.
What is Buffering?
Buffering is the act of temporarily storing data in a buffer. The buffer is a part of the main memory used to temporarily store or hold data sent between two devices. In simple terms, a buffer is a temporary holding place for data that is being sent from one location to another.
Buffering data has three main objectives. The first is that it helps in matching the pace of two devices between which data is transferred.
Second, it helps in the adaption of devices with different data transfer sizes to one another. It assists devices in manipulating data prior to sending or receiving it. The large message is divided into little parts and sent over the network in computer networking. The pieces are gathered in a buffer and reassembled to make a complete large message at the receiving end.
The final use of buffering is that it allows for copy semantics. It also supports the copy semantic, which means that the buffer data version and the data version at the time of the system call should be the same. It contributes to improving the device’s performance.
Features of Buffering
Various features of Buffering are as follows:
- It is a technique for overlapping I/O and single-job processing. When the data is read, and the CPU is about to start processing it, the input devices are directed to start the next input immediately.
- The CPU can continue processing the newly read data while the input device begins reading the data that follows. In this situation, the CPU generates data that is stored in a buffer until an output device can read it.
- It also supports the copy semantic, which means that the buffer data version and the data version at the time of the system call should be the same.
- It fixes the problem of the speed difference between the two devices through which the data is transferred.
Main Differences between the Spooling and buffering
Here, you will learn the main differences between spooling and buffering.
- Spooling is a type of multi-programming that allows users to copy data between several devices. On the other hand, buffering stores data in a memory area temporarily while processing other data.
- The basic operation of spooling is the overlap of one task’s input and output with the calculation of another task. In contrast, the general process of buffering is the overlapping of input and output from one function with the task count.
- A large area on the hard disk is available for the spooling operation to execute and then complete. In contrast, a small area with limited scope may be used for buffering.
- The buffering process takes less time to finish in comparison to spooling.
- Simultaneous peripheral operation online becomes another name for spooling, although buffering has no other name.
- The spooling is more efficient than the buffering.
- Furthermore, spooling helps in the exchange of data between devices with various data access rates. In contrast, the buffering assists in the adaptation to speed differences between data stream producers and consumers.
- Spooling needs less resource management than buffering because various resources control the process for different jobs. On the other hand, Buffering needs higher resource management than spooling because the same resource handles the process of the same divided job.
Applications/Implementations of Spool
- The most common can be found in I/O devices like keyboard printers and mouse. For example, In printer, the documents/files that are sent to the printer are first stored in the memory or the printer spooler. Once the printer is ready, it fetches the data from the spool and prints it. 最常见的是键盘打印机和鼠标等 I/O 设备。例如,在打印机中,发送到打印机的文档/文件首先存储在内存或打印机 spooler 中。一旦打印机准备就绪,它就会从 spooling 中获取数据并打印出来。
Ever experienced a situation when suddenly for some seconds your mouse or keyboard stops working? Meanwhile, we usually click again and again here and there on the screen to check if its working or not. When it actually starts working, what and wherever we pressed during its hang state gets executed very fast because all the instructions got stored in the respective device’s spool.
您是否遇到过鼠标或键盘突然停止工作几秒钟的情况?与此同时,我们通常会在屏幕上反复点击这里或那里,以检查其是否正常工作。当它真正开始工作时,由于所有指令都存储在相应设备的 spooling 中,我们在挂起状态下按下的内容和按下的位置都会被快速执行。
-
A batch processing system uses spooling to maintain a queue of ready-to-run jobs which can be started as soon as the system has the resources to process them. 批处理系统使用 spooling 来维护一个可随时运行的作业队列,一旦系统拥有处理这些作业的资源,就可以立即启动这些作业。
-
Spooling is capable of overlapping I/O operation for one job with processor operations for another job. i.e. multiple processes can write documents to a print queue without waiting and resume with their work. Spooling 能够将一个作业的 I/O 操作与另一个作业的处理器操作重叠,即多个进程可以将文件写入打印队列,无需等待,然后继续各自的工作。
-
E-mail: an email is delivered by a MTA (Mail Transfer Agent) to a temporary storage area where it waits to be picked up by the MA (Mail User Agent) 电子邮件:电子邮件由 MTA(邮件传输代理)传送到临时存储区,等待 MA(邮件用户代理)接收。
-
Can also be used for generating Banner pages (these are the pages used in computerized printing in order to separate documents from each other and to identify e.g. the originator of the print request by username, an account number or a bin for pickup. Such pages are used in office environments where many people share the small number of available resources). 也可用于生成 Banner 页面(这是计算机打印中使用的页面,用于将文件彼此分开,并通过用户名、账号或取件箱等标识打印请求的发起人。这种页面用于多人共享少量可用资源的办公环境)。