基本构成
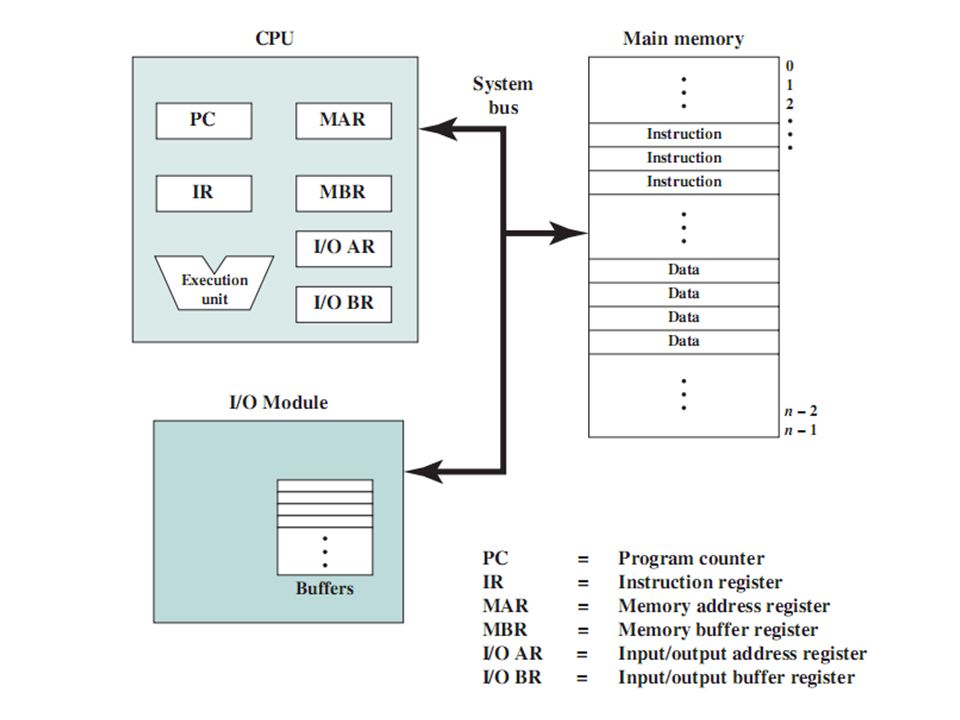
- CPU
- PC
- IR
- Execution unit
- MAR: Memory address register
- MBR: Memory buffer register
- I/O AR
- I/O BR
- I/O Module
- Buffers
- Main Memory
- Instruction
- Data
- System Bus
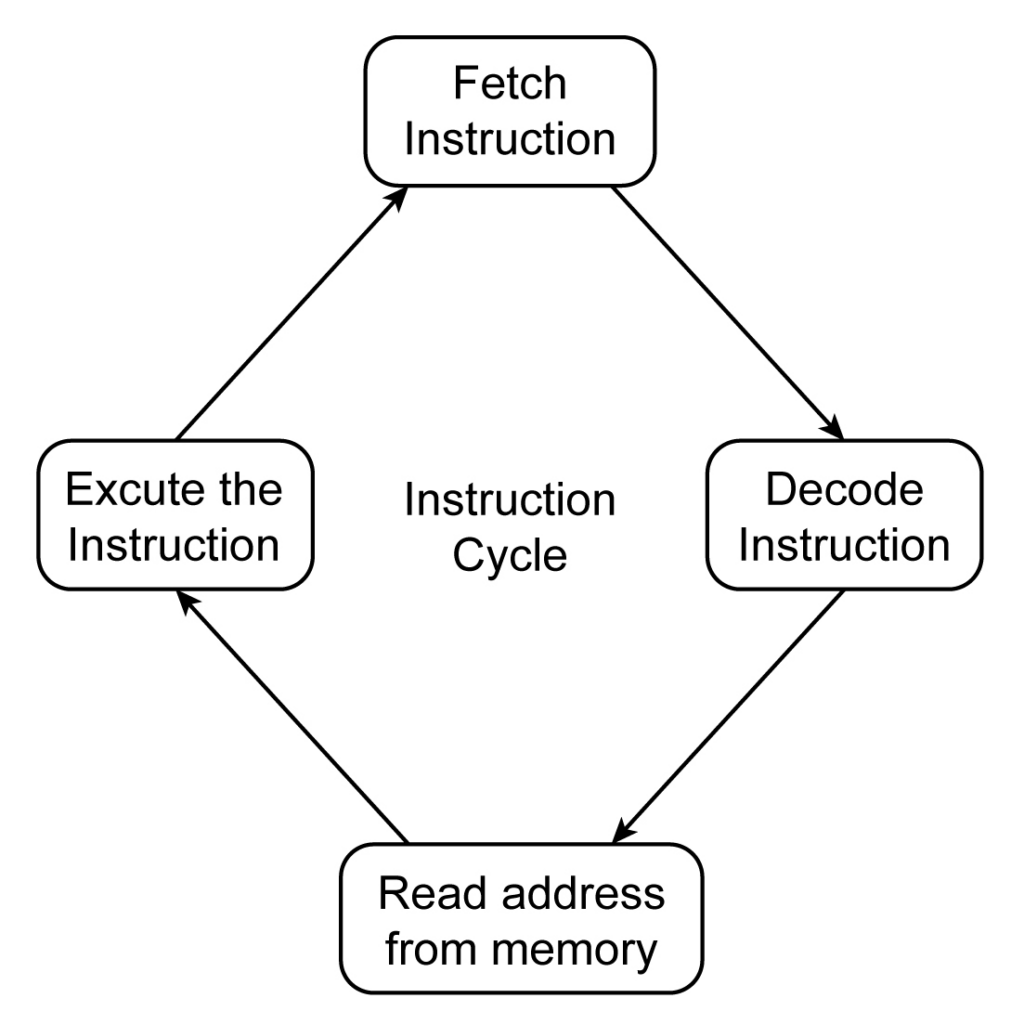
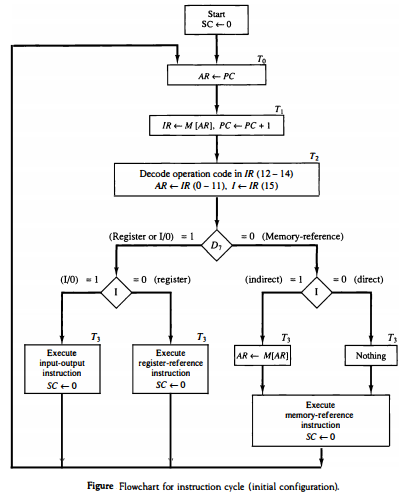
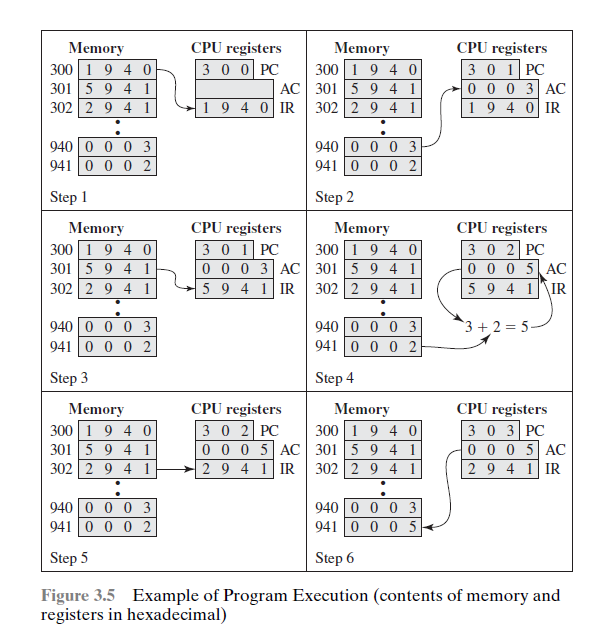
指令
指令周期
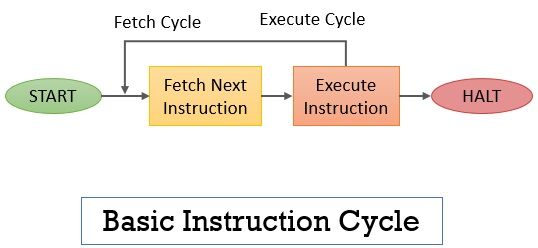
- Basic Instruction Cycle
- Start
- Fetch Next Instruction (Fetch Cycle)
- Execute Instruction (Execute Cycle, then goto Fetch stage)
- HALT
中断
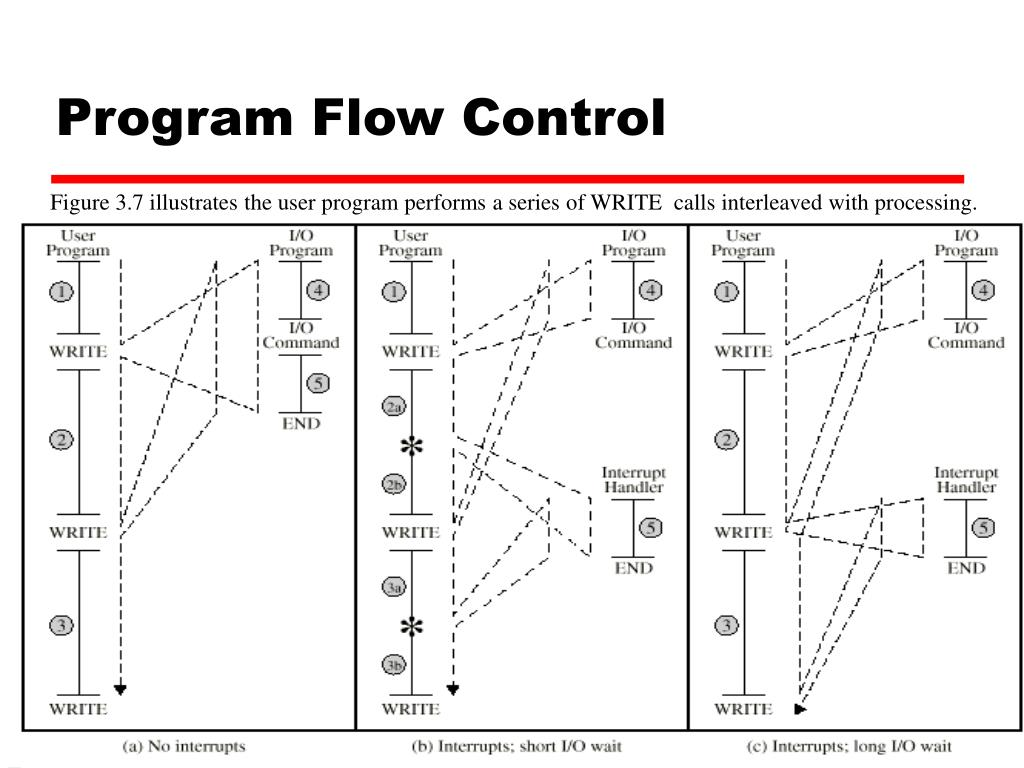
- No interrupts
- Interrupts: short I/O wait
- Interrupts: long I/O wait
中断和指令周期
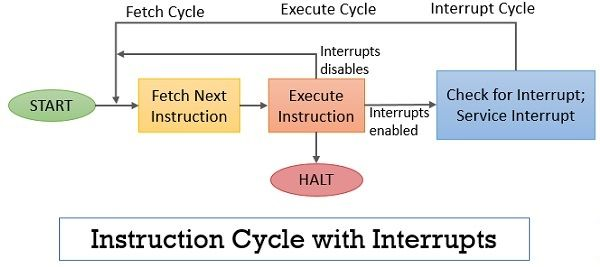
- 加入中断的指令周期
- START
- Fetch Next Instuction (fetch cycle)
- Execute Instruction (execute cycle)
- if interrupts disabled, jump to 2
- if interrupts enabled, jump to 4
- or HALT
- Check for interrupt; Service interrupt (interrupt cycle)
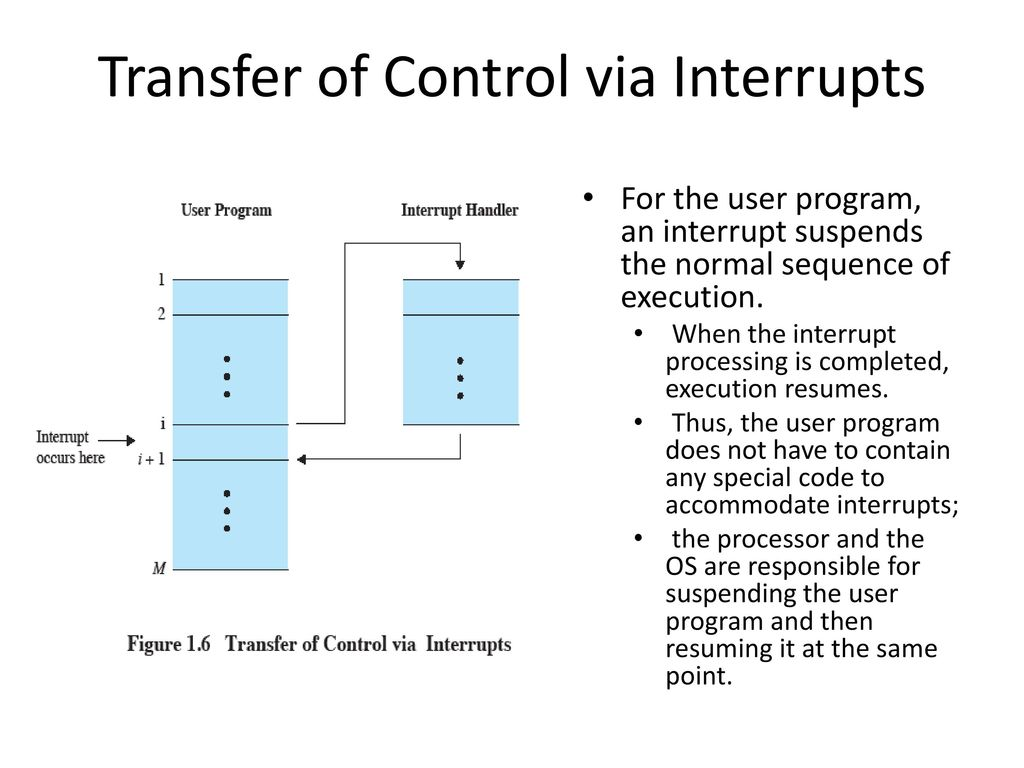
中断处理
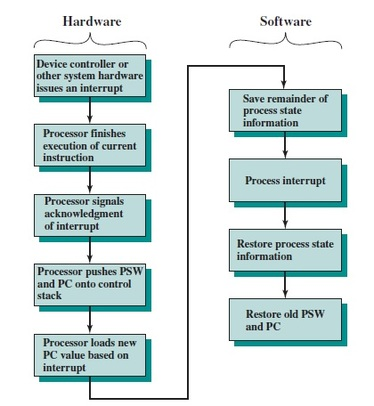
- 中断的典型处理顺序,
- 涉及软硬件协作,硬件负责处理 PC 和 PSW;
- Hardware
- Device controller or other system hardware issues an interrupt
- Processor finishes execution of current instruction
- Processor signals acknowledgment of interrupt
- Processor pushes PSW and PC onto control stack
- Processor loads new PC value based on interrupt
- Software
- Save remainder of process state infomation
- Process interrupt
- Restore process state information
- Restore old PSW and PC
- Hardware
多中断处理
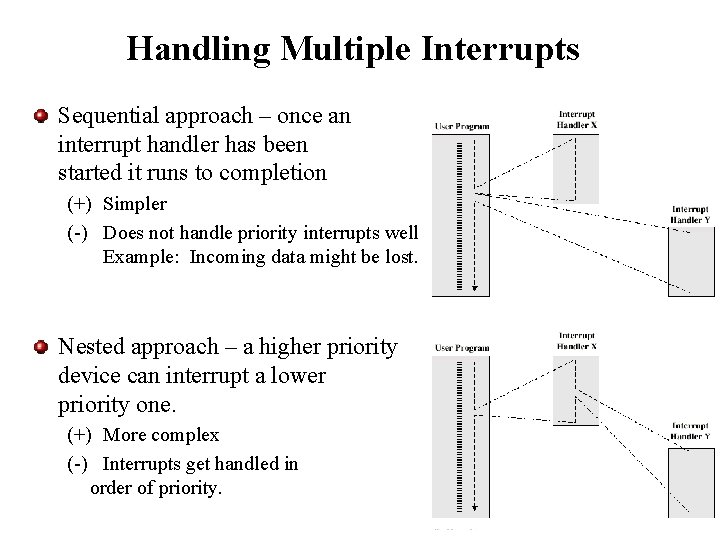
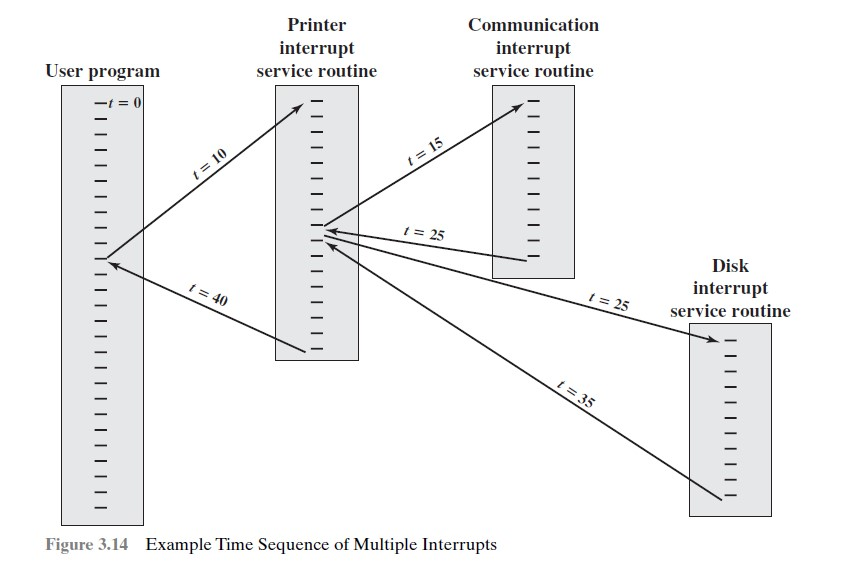
- 顺序处理和嵌套处理;
存储器层次结构
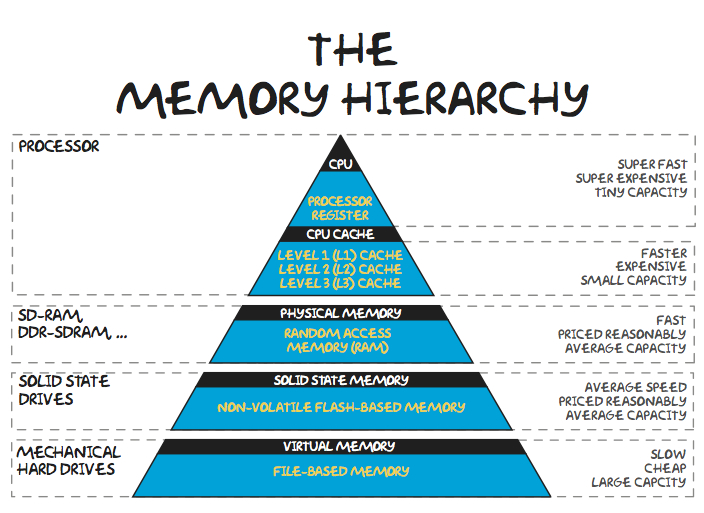
- Processor
- CPU: processor register
- Cache: L1, L2, L3
- SD-RAM DDR-SDRAM
- Physical memory: RAM
- Solid State Drives
- Non-volatile flash-based memory
- Mechanical Hard Drives (Virtual Memory)
- File-based memory
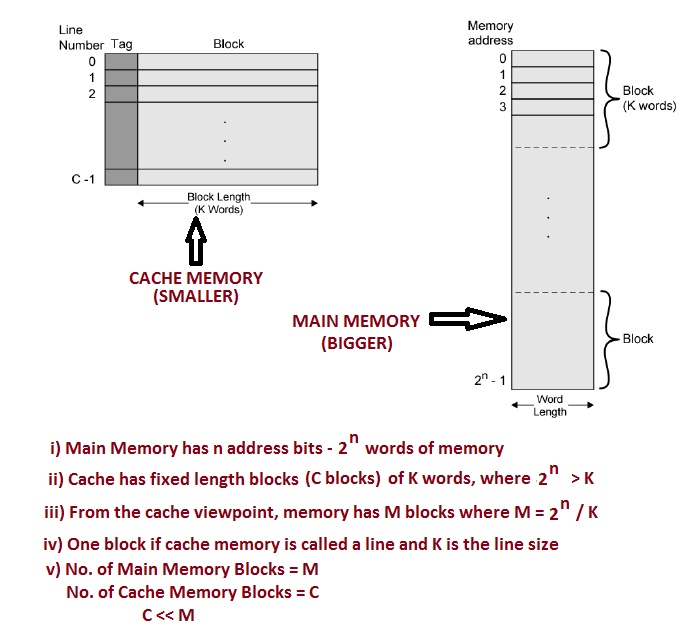
高速缓存
高速缓存结构
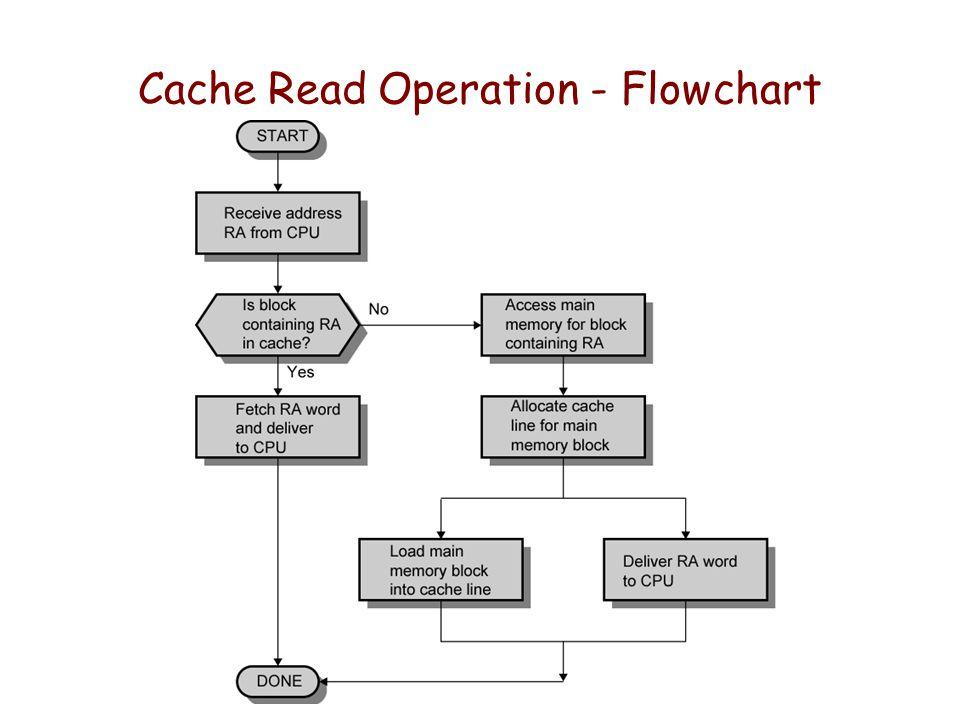
高速缓存读操作
高速缓存设计考虑因素
高速缓存大小
块大小
映射函数
置换算法
写策略
高速缓存级数
直接内存存取(DMA)
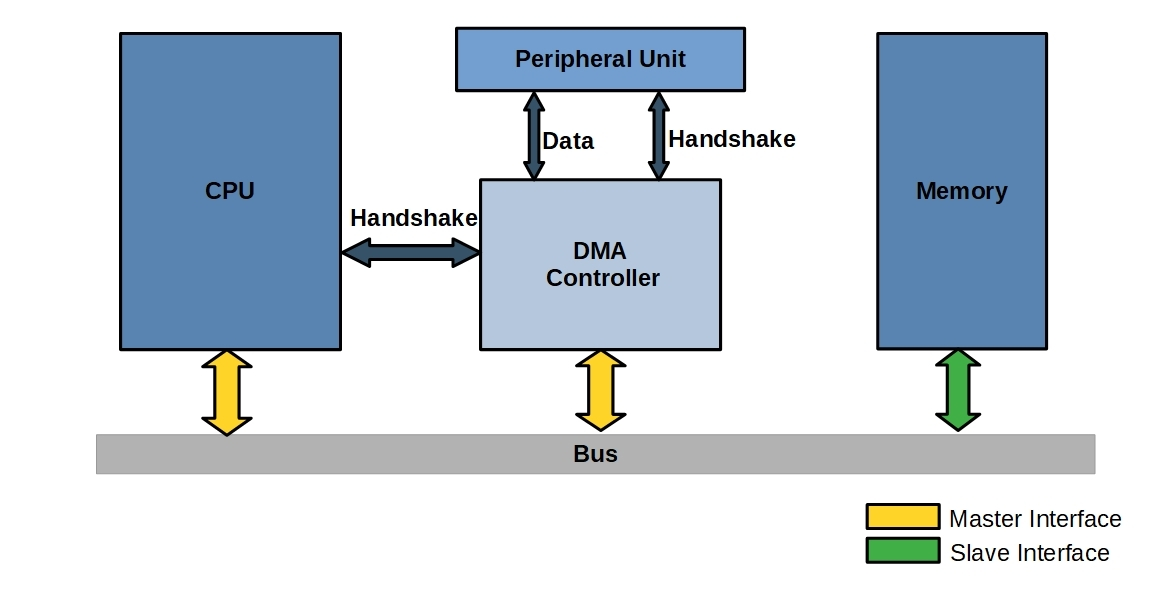
DMA 工作流程
指向原始笔记的链接
- 处理器需要读或写一块数据,则向 DMA 模块发送包含以下信息的命令
- 请求读 or 写操作的信号,通过 DMA 模块与 CPU 之间的读写控制线发送;
- 相关 I/O 设备的地址,通过数据线发送;
- 从存储器中读 or 向存储器中写的起始地址,通过数据线发送并保存在 DMA 模块的地址寄存器中;
- 读 or 写的字数,也通过数据线传送,保存在 DMA 模块的数据计数寄存器中;
- CPU 继续执行其他工作,I/O 任务完全由 DMA 模块执行,DMA 模块直接从存储器中(或向存储器)逐字传送整块数据
- 传送结束后,DMA 模块向 CPU 发送中断请求,CPU 执行中断处理例程
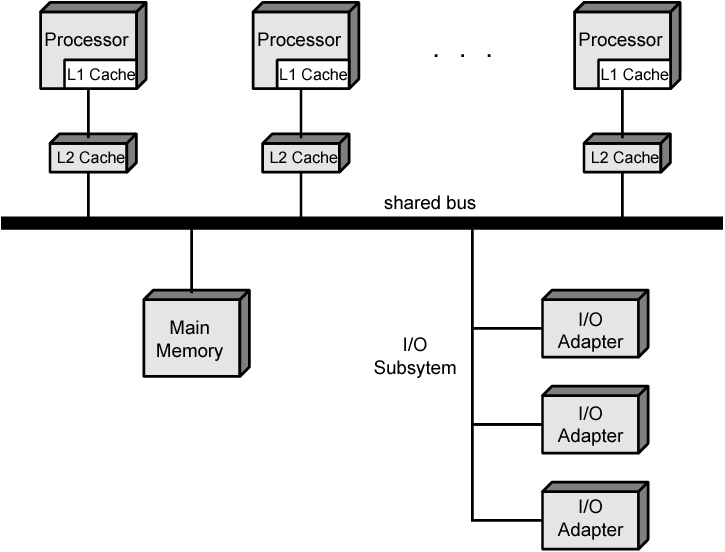
多处理器与多核计算机
对称多处理器SMP